Hey everyone anukram here 🙂 and today we will briefly discuss the IP address (internet protocol) and MAC (media access control) address.
I am pretty sure after reading the article you’ll be able to know the concept of IP and mac addresses and their use. So, Let’s start and see the concept of it by giving the simple definition of IP address
IP address
IP Address:- Internet Protocol Address is the unique identification of every device connected to any network whether it is public or private. Every device gets a unique IP in the particular network to identify itself with others devices and to communicate with each other they need it.
Any device that connects with any network will get an IP from its ISP for identifying the device and network traffic in the public or worldwide network. The IP is very necessary for any device validation on the internet for many things like communication with another device, file sending, and receiving.
An IP address is known as the logical address of the devices which is very necessary for device validation. Mostly the IP address is divided into classes which are likely to be A, B, C, D, and E class.
There are 2 types of IP address are available:-
- IPv4
- IPv6
IPv4
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) is the fourth version of internet protocol which basically uses a 32-bit address. IPv4 typically contains 4 octets in 32 bits. Every octet contains 8-bits of data and octets are commonly known as X.X.X.X. whereas a single X is referring to 1 octet of 8-bits. An IPv4 is like 192.168.0.1.
Mainly IPv4 is capable of providing 4 billion unique IPs to each device in the network, but it is not able to fulfill the requirement of our whole world. IPv4 is the first version of IPs which is launched for production on SATNET in 1982 and on ARPANET in January 1983.
IP class and Range
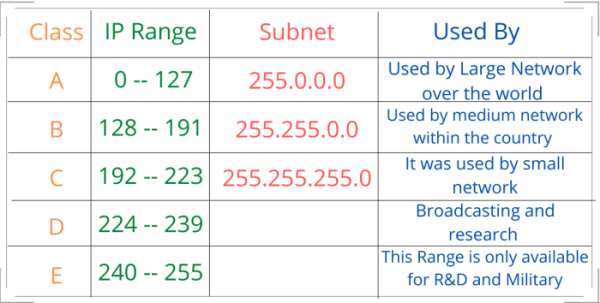
- Class A
- Class B
- Class C
- Class D
- Class E
- The range of class A IP is between 0 – 126. Whose subnet will be 255.0.0.0 Class A IP is used by large network companies over the world for distributing the internet in the whole world.
- IP 127 is used for the local host or local server as it is known as loopback IP.
- The range of class B IP lies between 128 and 191, with a subnet likely being 255.255.0.0. this IP class is used by medium network companies for distribution within the country.
- The range of class C IP lies between 192 – 223, whose subnet is likely to be 255.255.255.0. this IP class is used by small network distributors company or used as a private network inside the organization.
- Class D IP range lies between 224 – 239. which is commonly used for broadcasting and research purpose.
- Class E IP range lies between 240 – 255. which is only available for research development and military purpose.
IPv6
IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) is the upgraded version of IP’s protocol and is better than IPv4 because it can serve more than 340 trillion unique IP addresses to each device. This typically contains 128 bits in 8 octets. Every octet ion IPv6 has 16 bits which is a total of 128 bits. As we know it serves 340 trillion IP’s which is more than enough to fulfill the requirement of every device in our world.
For example- 2004:daca:0000:0000:0000:0000:3421:abae which can be expressed as 2004:daca::3421:abae. in this (::) the double colon represents the zero in between them.
Difference between IPv4 and Ipv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| Internet protocol version 4 | Internet protocol version 6 |
| It uses 32-bits | It uses 128-bits |
| Capable of generating 4 billion unique IPs | Capable of generating around 340 trillion unique IPs |
| Contains decimal digits separated with (.) dots | Contains hexadecimal numbers separated with (:) colon |
| The range lies between 0-255 | The range lies between 0-FFF (65535) |
| Contains 4 octets each has 8-bits | Contains 8 octets each has 16-bits |
| It has 5 classes for classification | It doesn’t contain any class |
IP types
As we know IP are useful for communication, data, and information transfer between networks and machines. So as seeing the requirement IP’s are classified into four major categories for different purposes.
Four types of IP are
- Private IP
- Public IP
- Static IP
- Dynamic IP
Private IP
Private IP’s are also known as the local IP address of any person or organization. This IP will be private IP which is referred to as a private network within the premises of any organization which is not accessible off-premises because it is private within the organization and not publicly available for all. Basically, private IP’s are local IP addresses that cannot be able to connect with the internet. But private IP’s are useful to communicate within the network and share data within the premises. Basically, organizations use private IP’s to secure their data from public access and communicate with each other securely inside the organization for data and information sharing without any public internet.
Privates IP are also useful for making well-labeled labs and computer network inside the organization which is easily traceable and secure within the premises.
Classes and ranges in private IP
- Class A, its range is between 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 (1 network)
- Class B, its range is between 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 (16 networks)
- Class C has 256 networks with a range between 192.168.0.0 to .192.168.255 (256 networks)
Public IP
Class A, B, and C IPs are publicly available by IANA Internet Assing Number Authority. Public IP are accessible anywhere in the world via the internet. Every server and website are having a unique public IP address for accessing them from anywhere on the internet.
You can check your public IP address by searching on Google whatismyipaddress
Static IP
Static IP is also known as the dedicated IP of a particular user which is assigned them to access the internet by their ISP. Static IP means a fixed IP address that cannot be changeable. Static is the unique address provided by the ISP (internet service provider) to the user for their validation on the internet.
Dynamic IP
Unlike dedicated IP the dynamic IP will change every time when you connect to the network. Every time user will get a new and unique IP address in the network from the device like a router for accessing the internet or network. But if you connect to the internet static IP will remain the same for the router.
Dynamic IP is not fixed it changes from time to time. This IP is dependent upon the router or access point to the device which is connecting with them.
MAC address
Media Access Control (MAC) address is the fixed unique identification number of the devices for their local identification on the internet. Basically, a mac address contains the information of the device manufacturing company name serial number, and unique identification of the particular device.
MAC address is common in most IEEE 802 networking technology which includes internet cards, Wi-Fi adapters, and Bluetooth chips.
As an IP address, a MAC address is also used for the identification of the device on the internet. But MAC is somewhat different because it is the Physical address of the device and the IP address is the logical address of the device which may be changeable after some time. But you can not MAC address of any device.
If you have any queries regarding the above content, or you want to update anything in the content, then contact us with your queries. You can directly post your question in the group.
Connect with us on these platforms