The OSI model (or Open Systems Interconnection Model) is an absolute fundamental model used in networking. This critical model provides a framework dictating how all networked devices will send, receive and interpret data.
Room Link OSI Model
One of the main benefits of the OSI model is that devices can have different functions and designs on a network while communicating with other devices. Data sent across a network that follows the uniformity of the OSI model can be understood by other devices.
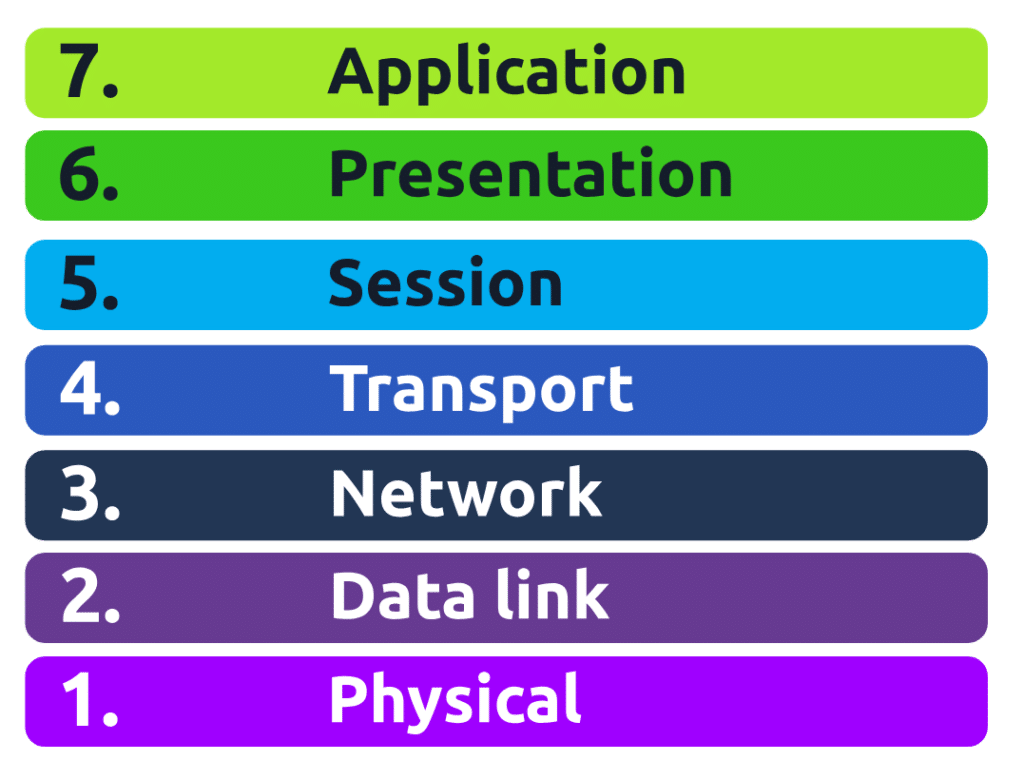
The OSI model consists of seven layers which are illustrated in the diagram below. Each layer has a different set of responsibilities and is arranged from Layer 7 to Layer 1.
At every individual layer that data travels through, specific processes take place, and pieces of information are added to this data, which is what we’ll come to discuss in the upcoming tasks within this room.
However, for now, we only need to understand that this process is called encapsulation and what the OSI model looks like in the diagram below:
Question: What does the “OSI” in “OSI Model” stand for?
Answer: Open System Interconnection
Question: How many layers (in digits) does the OSI model have?
Answer: 7
Question: What is the key term for when pieces of information get added to data?
Answer: Encapsulation
Task 2 Layer 7 Application
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Application
Question: What is the technical term that is given to the name of the software that users interact with?
Answer: graphical user interface
Task 3 Layer 6 Presentation
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Presentation
Question: What is the main purpose that this Layer acts as?
Answer: Translator
Task 4 Layer 5 Session
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Session
Question: What is the technical term for when a connection is successfully established?
Answer: Session
Question: What is the technical term for “small chunks of data”?
Answer: Packets
Task 5 Layer 4 Transport
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Transport
Question: What does TCP stand for?
Answer: Transmission Control Protocol
Question: What does UDP stand for?
Answer: User Datagram Protocol
Question: What protocol guarantees the accuracy of data?
Answer: TCP
Question: What protocol doesn’t care if data is received or not by the other device?
Answer: UDP
Question: What protocol would an application such as an email client use?
Answer: TCP
Question: What protocol would an application that downloads files use?
Answer: TCP
Question: What protocol would an application that streams video use?
Answer: UDP
Task 6 Layer 3 Network
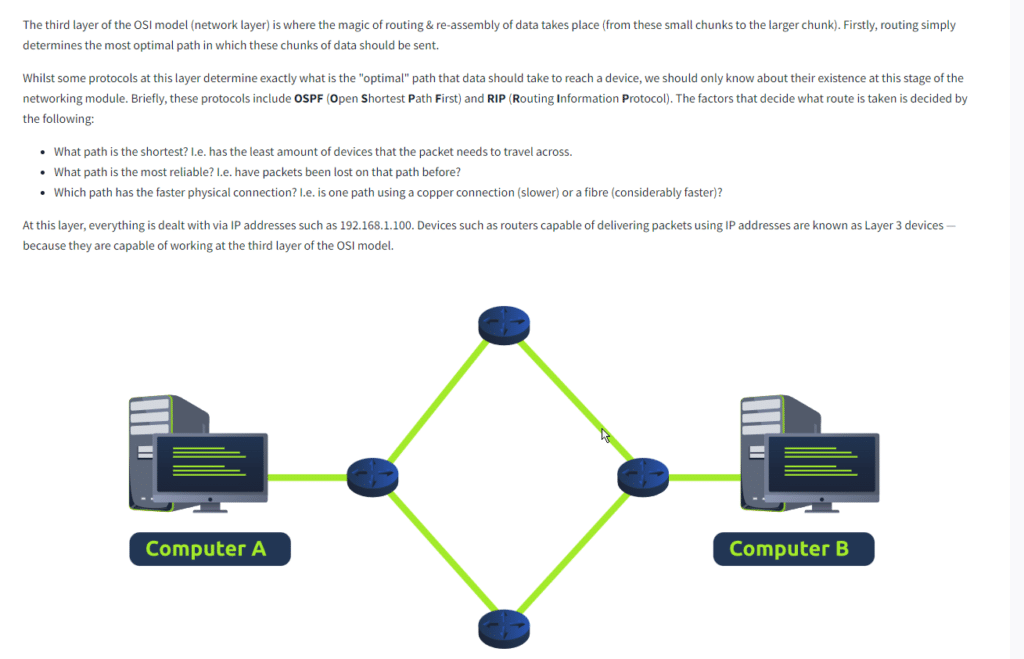
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Network
Question: Will packets take the most optimal route across a network? (Y/N)
Answer: Y
Question: What does the acronym “OSPF” stand for?
Answer: open shortest path first
Question: What does the acronym “RIP” stand for?
Answer: routing information protocol
Question: What type of addresses are dealt with at this layer?
Answer: ip addresses
Task 7 Layer 2 Data Link
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: data link
Question: What is the name of the piece of hardware that all networked devices come with?
Answer: network interface card
Task 8 Layer 1 Physical
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Physical
Question: What is the name of this Layer?
Answer: Binary
Question: What is the name of the cables that are used to connect devices?
Answer: ethernet cable
Task 9 Practical OSI Game
Can you escape the OSI dungeon? Climb the levels in the correct order to escape the dungeon and reveal the flag! (Can you beat our staff high score of 19 seconds?)
Click the “View Site” button on the right to start.
Question: Escape the dungeon to retrieve the flag. What is the flag?
Answer: THM{OSI_DUNGEON_ESCAPED}
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!